Taking it From the Top:
Optical fiber uses light instead of electricity to carry a data signal. This is unique because fiber can carry high bandwidth signals over long distances without degradation. Copper can also carry high bandwidth, but only for a few hundred yards – after which the signal begins to degrade and bandwidth narrows. Optical fiber has been used in communication networks for more than 30 years, mostly to carry data traffic from city to city or country to country. With its advantages over copper, fiber optic networks have revolutionized long-distance phone calls, cable TV and the Internet.
However, to many people, even veterans of the industry, there are many industry terms that are still mysterious or unclear. Don’t worry, at Multicom we believe in keeping it simple. Let’s try to make sense of it from the beginning:
Let's Begin with Fibers
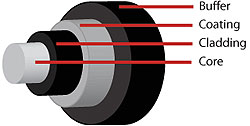 Optical Fiber: Thin strands of highly transparent glass or sometimes plastic that guide light.
Optical Fiber: Thin strands of highly transparent glass or sometimes plastic that guide light.
Core: The center of the fiber where the light is transmitted.
Cladding: The outside optical layer of the fiber that traps the light in the core and guides it along – even through curves. This layer is never stripped off the fiber.
Buffer Coating or Primary Coating: A hard plastic or acrylic coating on the outside of the fiber that protects the glass from moisture or physical damage.
Mode: A single electromagnetic field pattern (like a ray of light) that travels in fiber.
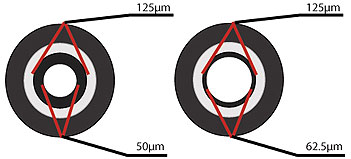
Multi-mode Fiber
Multi-mode Fiber: Has a bigger core (almost always 62.5 microns – a micron is one one-millionth of a meter – but sometimes 50 microns) and is used with LED sources at wavelengths of 850 and 1300 nm for short distance, lower speed networks like LANs (Local Area Networks).
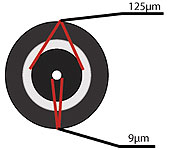
Singlemode Fiber
Singlemode Fiber: Has a much smaller core, only about 9 microns, and is used for telephony and CATV (Cable TV) with laser sources at 1300 and 1550 nm. It can go very long distances at very high speeds but with higher cost.
Terms for Termination
Fiber termination is an important part of fiber optic cabling. Having an idea of these terms in termination will help:
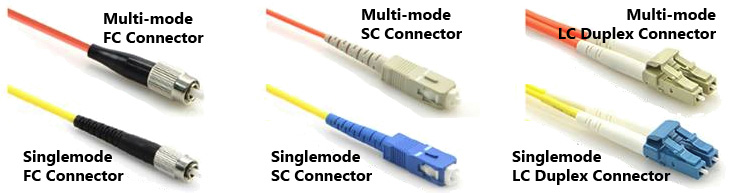
Multi-mode has orange cable, Singlemode has yellow cable
Connector: A non-permanent device for connecting two fibers or fibers to equipment where they are expected to be disconnected occasionally for testing or rerouting. It also provides protection to both fibers.
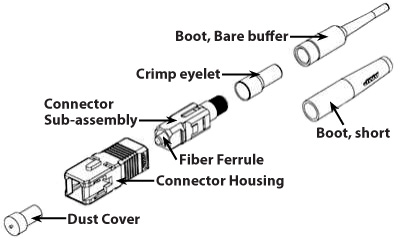
Components of an SC Connector
Ferrule: A tube that holds a fiber for alignment, usually part of a connector.
Splice: A permanent joint between two fibers.
Mechanical Splice: A splice where the fibers are aligned and joined by a mechanical splice device.
Fusion Splice: A splice created by welding or fusing two fibers together.
Cable Management: Terminations and Splices require some hardware for protection and management: patch panels, splice closures, ODF (optical distribution frame), FTB (fiber termination box) etc.
Let's Get a Little Technical - In a Simple Way
Some of these terms you may be familiar with by knowing coiax cabling, but they vary in reference to fiber optics, so let’s review:
Save time and money. Multicom has Certified Fiber to the Home Professionals (CFHP) on staff who can take all of this into account and design the system that’s right for you.
Attenuation: The reduction in optical power as it passes along a fiber, usually expressed in decibels (dB).
Bandwidth: The range of signal frequencies or bit rate within which a fiber optic component, link or network will operate.
Decibels (dB): A unit of measurement of optical power, which indicates relative power. A -10 dB means a reduction in power by 10 times, -20 dB means another 10 times or 10 times overall, -30 means another 10 times or 1000 times overall and so on.
- dB: Optical power referenced an arbitrary zero level.
- dBm: Optical power referenced to 1 milliwatt.
Micron (um): A unit of measure used to measure wavelength of light.
Nanometer (nm): A unit of measure used to measure the wavelength of light (meaning one one-billionth of a meter).
Optical Loss: The amount of optical power lost as light is transmitted through fiber, splices, couplers, etc, expressed in dB.
Optical Power: is measured in “dBm”, or decibels referenced to one milliwatt of power. while loss is a relative reading, optical power is an absolute measurement, referenced to standards. You measure absolute power to test transmitters or receivers and relative power to test loss.
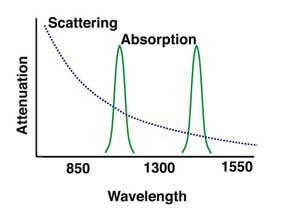
Absorption: Absorption occurs in several specific wavelengths called water bands due to the absorption by minute amounts of water vapor in the glass.
Scattering: The change of direction of light after striking small particles that causes loss in optical fibers and is used to make measurements by an OTDR
Wavelength: A term for the color of light, usually expressed in nanometers (nm) or microns (m). Fiber is mostly used in the infrared region where the light is invisible to the human eye.
At Multicom, we strive to not only provide you with the products needed for the end to end integration of a fiber optic and CATV distribution systems; but most importantly, we stress ‘personal service’. When you call us a real person answers the phone! You will be then be transferred to a qualified sales or technical engineer with the experience and expertise to provide the products and service you need, or answer your questions. We value the relationships we have built over the 33 years we have been an industry leader.
